Captcha is short for "Completely Automated Public Turing Test to tell Humans and Computers apart". That means captchas are supposed to decide whether a user of a website is a human or for example a bot.
What are Captchas used for?
The differentiation between a person and a bot is mostly used for online forms like contact forms, surveys, guestbooks and the registration of an e-mail address for example for a newsletter. In these cases it is especially important to decide if an entry was made by a human or a bot because in this context bots are usually used to spread spam. This is why they are also called spambots. Human entries normally have a reasonable motive. As a result webmasters try to make filling out a form on their website impossible for bots and meanwhile comfortable for real users. This often causes problems because human visitors of a website may be annoyed by captchas which for example require a difficult entry that takes time.
What different Kinds of Captchas are there?
Over the last years many different kinds of captchas have been invented because bots became more intelligent and users wanted different solutions:
- Writing down one or several words: These captchas show one or more words as an image that are distorted an hard to read. The user has to write down these words in a special field to complete the form and for example send an e-mail to the webmaster.
- Typing in numbers: This kind of captcha works as the first one. The only difference is that a user has to decipher numbers instead of words.
- Arithmetical problems: If a webmaster uses this type of captcha users have to solve a simple arethmetical problem like for example "8 + 2" and insert the result in a provided field.
- Solve a mystery: Another option is to describe a special object. A user than has to find out the answer. For example: A piece of jewellery worn on the finger. The solution would be a ring.
- Picture puzzles: A new method to decide between a bot and a human user is to show several pictures with totally different or related motifs. Showing related pictures a task may be to find the difference between two pictures. If a user sees different pictures he has to answer a question like: "Which picture shows a lion?" by clicking on the right photo.
- Listening: As all captchas explained until now are not suitable for visually handicapped users there is also a possibility to play a sound for example a word read to a user. Then this word has to typed into the field.
Beside these methods there are also possibilities to differentiate between bots and humans without involving the visitors of your website:
- Minimum fill out time: Usually bots fill out forms very fast. Much faster than humans because they don't think about what they want to write. They spot how many fields a form has and then fill in their spam. As a result a minimum fill out time of about 8 to 10 seconds is enough to detect a bot. A human would need much more time to type in his e-mail adress and concerns or reviews.
- Bot trap: By crawling forms bots recognize every field and fill out each. By adding a special field which is invisible for human visitors bots can be identified because no real user can fill out a field he cannot see. In contrast, bots will notice and therefore fill out the hidden field.
- DNSBL: This is short for DNS Blackhole List. This kind of captcha uses a list of known spam hosts. If a form is filled out by a bot whose IP adress is contained in such a list the form and its content will be rejected.
Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard for your Joomla! Website
Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard is a Joomla! extension which offers several kinds of captchas to the webmaster. The most important thing to mention is that all included captchas do not require any action of the website's visitors. For this reason it is possible to be protected from spam and at once to have content users who are not annoyed by filling out fields with words or numbers they can hardly read.
Which Captchas are included?
The extension includes the following types of captchas already mentioned before:
- Minimum fill out time
- Bot Trap
- DNSBL
While the other protection mechanisms can also be used with the free version of the extension, the DNS Blackhole Lists are a pro feature.
How to install Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard on your Joomla! Website
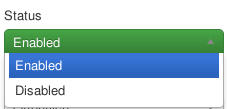
First you have to download the extension and install it as usual. Afterwards the plugin has to be enabled. If you have just installed the extension you can click on the "Configure plugin now" button to reach the configuration. Alternatively you can click on "Extension" in the main menu of your Joomla! backend and there choose "Plugins". Now you can click on Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard in the list of installed plugins. On this site you first change the status from "disabled" to "enabled".
Now you can decide which of the described protection mechanisms you want to choose. You can select any possible combination but at least one of the methods has to be enabled.
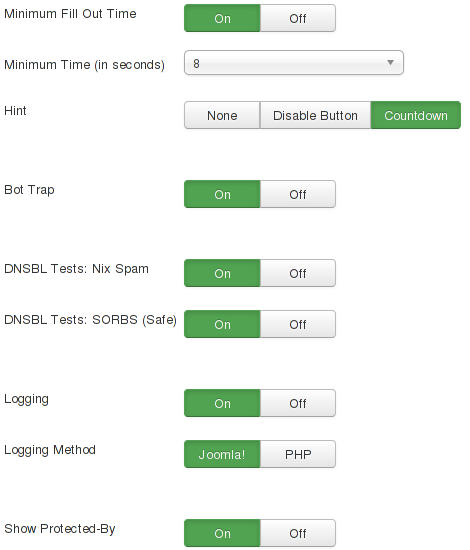
Just like the DNSBL Tests the Hint is a pro feature. If this is enabled in combination with for example the Minimum fill out time users can get a hint for how long they have to wait until a message can be sent.
If you have completed and saved the configuration the last step is to tell Joomla! that you want to use Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard as your default captcha. You can do so by clicking on "System" in the main menu of your Joomla! backend. There choose "Global Configuration" and change the "Default Captcha" to Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard.
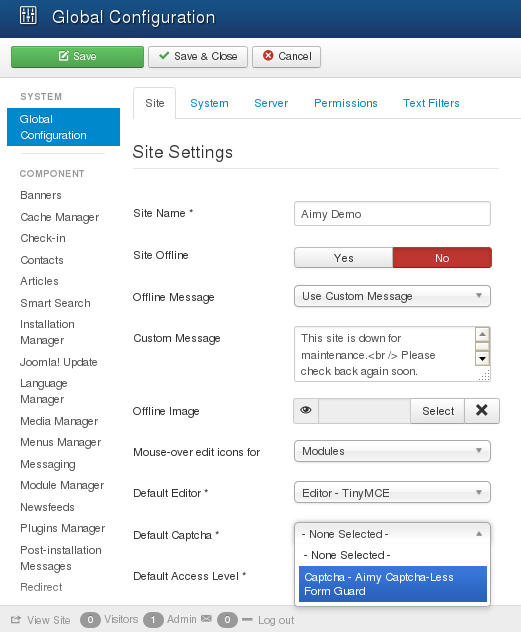
Aimy Captcha-Less Form Guard is then used as a default captcha for your Joomla! website and will be used whenever an extension requests the default captcha to be displayed. For further information you can read the user manual.
